Numbers
- Unitless integers and decimals which have meaning in different context
- Used in:
opacity: percentage, 0.5 represents 50% opacityline-height: ratio, 1.5 represents 1.5 times the original font sizergb(): color value between 0 and 255
Absolute Lengths
- An absolute length is calculated against a single shared base value
cm, mm, inpx
Relative Lengths
- A relative unit is compared against a base value that can change.
- Examples:
ch, em, remvw, vh, vmin, vmax
Font
ch
ch unit = font width of 0 as a character- Helpful in keeping paragraph size controlled
em
em unit = font size (Height)- traditionally it used to be height of “M” hence the name
em
rem
rem unit = font size (Height) of the root element
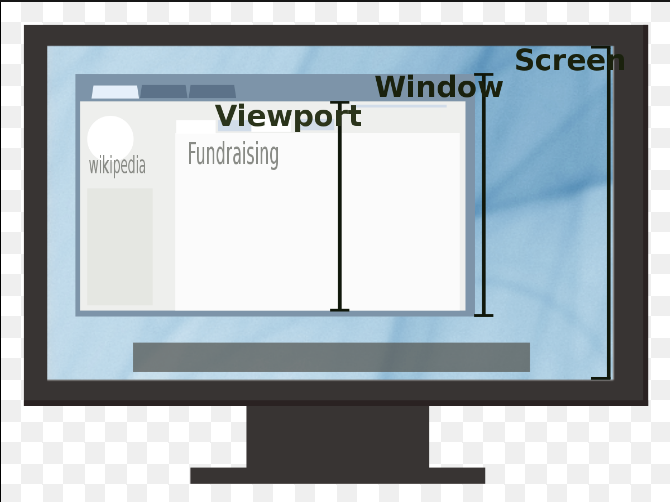
Viewport
- https://web.dev/blog/viewport-units
vw: 1% of viewport widthvh: 1% of viewport height- The above units do not work well with mobile which includes address bar
- Modern Units:
vi: 1% of viewport in root element inline axisvb: 1% of viewport in root element block axisvmax: 1% of viewport larger dimensionvmin: 1% of viewport smaller dimension
Terminology
- Root element: It is a pseudo element defined by
:root which specifies the highest element in the tree
- In case of HTML it is
<html> element
- It can be used to declare global variables
- Viewport: User’s visible area of the webpage
- It can change while resizing browser window
- github.com is responsive and behaves differently on browser resize
- google.com is not responsive and overflows the website instead if browser is resized