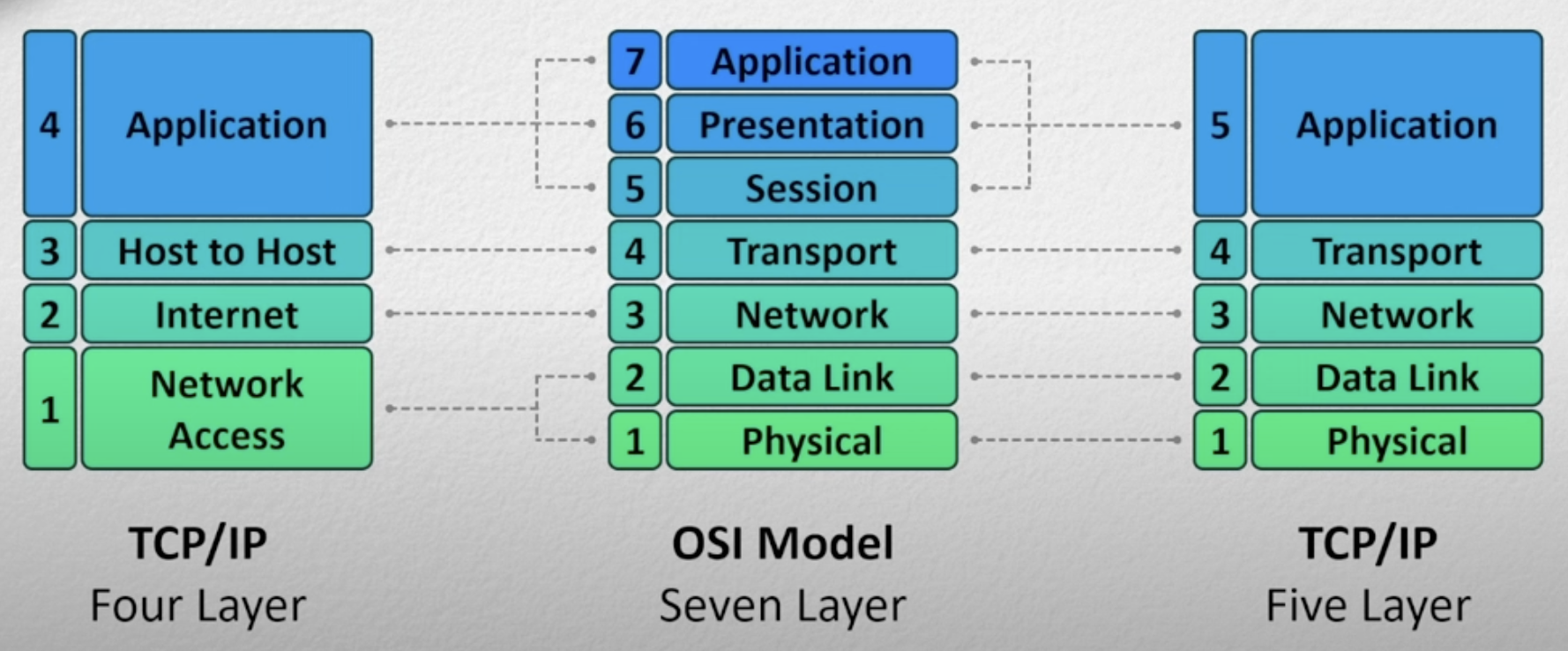
OSI
- Open System Interconnection model
- It is a general model and has 7-layers
- Application
- Presentation
- Session
- Transport
- Network
- Data Link
- Physical
| Layer | Name | Devices | Protocols | PDU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | Application | About: What interpreted characters do Using ASCII in L6 you interpret GET /simplewhich will mean GET request on /simple endpoint | HTTP, SMTP, FTP DHCP, DNS, Telnet | |
| 6 | Presentation | About: Interpreting 1s and 0s Encoding/Decoding for example ASCII, Encryption/Decryption, Compression/Decompression | TLS, SSL, MIME | |
| 5 | Session | RPC???, NetBIOS | ||
| 4 | Transport | About: Service to Service delivery Achieved using Ports+Other info Data streams is routed to correct program | TCP, UDP | Segment |
| 3 | Network | About: End-to-End delivery Routers, Hosts, Anything with IP Bridge and other L1, L2 devices may have IP address but not required for its operation | IP Address ICMP | Packet |
| 2 | Data Link | About: Hop-to-Hop delivery NIC Card, WiFi Access Card, Switch, Bridge Routers have multiple NICs | MAC address - Ethernet (802.3) - WiFi (802.11) ARP | Frame |
| 1 | Physical | About: Transporting Bits Devices: Repeaters, Hubs, WiFi Wires and Cables: Ethernet, Fiber, Coaxial | Ethernet (IEEE 802.3), Wifi (IEEE 802.11), USB, Infrared | Frame |
- Notes
- IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11, USB are all specs and contain multiple protocols that can span multiple layers in OSI model
- routers or in general other devices may work with multiple layers, OSI model is just conceptualization not rigid rules
- TCP and UDP protocols have ports in their specification which is used to distinguish different data streams with programs
- Layer 5, 6, 7 are considered universally as Application Layer
- Layer 1, 2 are combined as Network Access Layer in TCP/IP-5 layer model
TCP/IP
- protocol based model
- were built to offer highly reliable end-to-end data delivery over an unreliable network, such as the internet.
- incorporates the rules created when the internet developed
- The names of layers are not consistently used everywhere
- Application Layer
- Transport Layer
- Internet Layer
- Network Access Layer
Common TCP/IP Layer Names
- 4 Layer Model
| Layer | Most Common Name | Alternate Names |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | Application | Application/Presentation |
| 3 | Transport | Host-to-Host |
| 2 | Internet | Network, Networking |
| 1 | Network Access | Data Link, Physical, Network Interface, Link |
- 5 Layer Model
| Layer | Most Common Name |
|---|---|
| 5 | Application |
| 4 | Transport |
| 3 | Network |
| 2 | Data Link |
| 1 | Physical |