Router
- It has IP and MAC address on each NIC
- Since it has to connect to two different networks it must have different IPs simultaneously, hence multiple NICs are required
- Internet is nothing but a bunch of routers
Routing Table
- Routing Table is stored in router or network host
- When Routers receive packets with an unknown Destination IP, packet is dropped
- Hence, Routing Table must be populated ahead of time unlike ARP Cache
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Routing_table
- MacOS routing table
netstat -rn
Routing tables
Internet:
Destination Gateway Flags Netif Expire
default 10.119.41.223 UGScg utun4
default 192.168.31.1 UGScIg en0
default link#25 UCSIg bridge100 !
10.119.11.1 10.119.41.223 UGHS utun4
10.119.41.223/32 127.0.0.1 UGSc lo0
13.107.64/18 192.168.31.1 UGSc en0
52.112/14 192.168.31.1 UGSc en0
52.122/15 192.168.31.1 UGSc en0
127 127.0.0.1 UCS lo0
127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1 UH lo0
165.85.126.240 192.168.31.1 UGHS en0
192.168.31 10.119.41.223 UGdCSc utun4
route print
Populating Routing Table
- It can be populated by 3 methods
- Directly Connected
- Routes for the Networks which are attached
- Static routes
- Routes manually provided by an Administrator
- Dynamic routes
- Routes learned automatically from other Routers
- Exact method to learn is governed by different protocols called Dynamic Routing Protocols
| Destination Network ID | Next Hop |
|---|
| DC | 10.0.55.x /24 | Left |
| DC | 10.0.44.x /24 | Right |
| Dyn. or Static | 10.0.66.x /24
(This network is not directly available) | 10.0.55.2
(Another router’s IP address) |
Default Gateway
Getting IP address of WiFi router
- Look for default gateway
- MacOS - List routing table entries
- Windows
Getting strength of Wifi
Router Hierarchy
- Routers are typically connected in a hierarchy
- Helps network easier to scale
- Helps to have more consistent connectivity
- Hierarchy allows for Route Summarization
- Reduce the number of Routes in Routing Table
- Default Route - Ultimate route summary
0.0.0.0/0 — for everything else go here
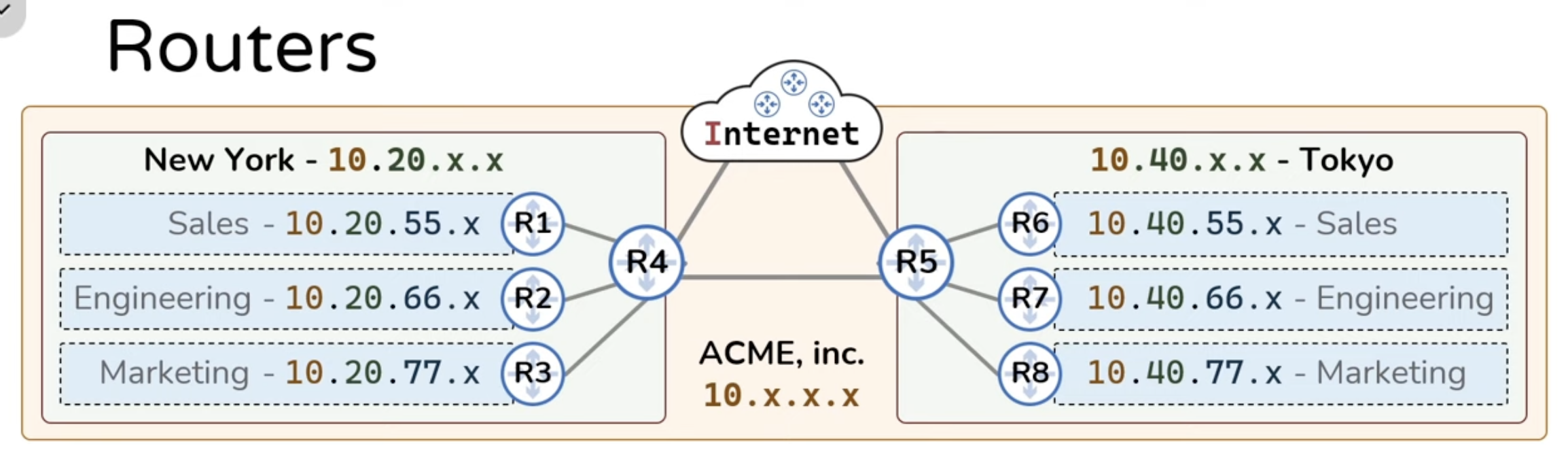
R5 Routing Table
| Destination Network ID | Next Hop |
|---|
| 10.40.55.0/24 | R6 |
| 10.40.66.0/24 | R7 |
| 10.40.77.0/24 | R8 |
| 10.20.55.0/24 | R4 |
| 10.20.66.0/24 | R4 |
| 10.20.77.0/24 | R4 |
- After Route Summarization
| Destination Network ID | Next Hop |
|---|
| 10.40.55.0/24 | R6 |
| 10.40.66.0/24 | R7 |
| 10.40.77.0/24 | R8 |
| 10.20.0.0/16 | R4 |
R8 Routing Table
| Destination Network ID | Next Hop |
|---|
| 10.40.77.0/24 | DC |
| 10.40.55.0/24 | R5 |
| 10.40.66.0/24 | R5 |
| 10.20.55.0/24 | R5 |
| 10.20.66.0/24 | R5 |
| 10.20.77.0/24 | R5 |
- After Route Summarization
| Destination Network ID | Next Hop |
|---|
| 10.40.77.0/24 | DC |
| 10.0.0.0/8 | R5 |
| Destination Network ID | Next Hop |
|---|
| 10.40.77.0/24 | DC |
| 0.0.0.0/0 | R5 |
